Learn the difference between simple, compound and complex sentences with anticipations, interruptions, and afterthoughts. In just 17 minutes, you will know how to punctuate and structure every sentence you will ever want to write.
This article can also help you understand how to avoid common errors like fragment, run-on, and comma splice errors because understanding sentence structure is key to understanding punctuation, also. Writing concise sentences by being mindful of sentence structure will also help you avoid wordiness.
Watch the Video
Learn the difference between a simple sentence, a compound sentence, and a complex sentence in 17 minutes by watching this video. You will never need another explanation.
Simple, Compound, and Complex Sentences
There are three basic sentences types. They get their names from their structures. The structures can be either simple, joined as equals, or joined with a subordinate. I’ll explain.
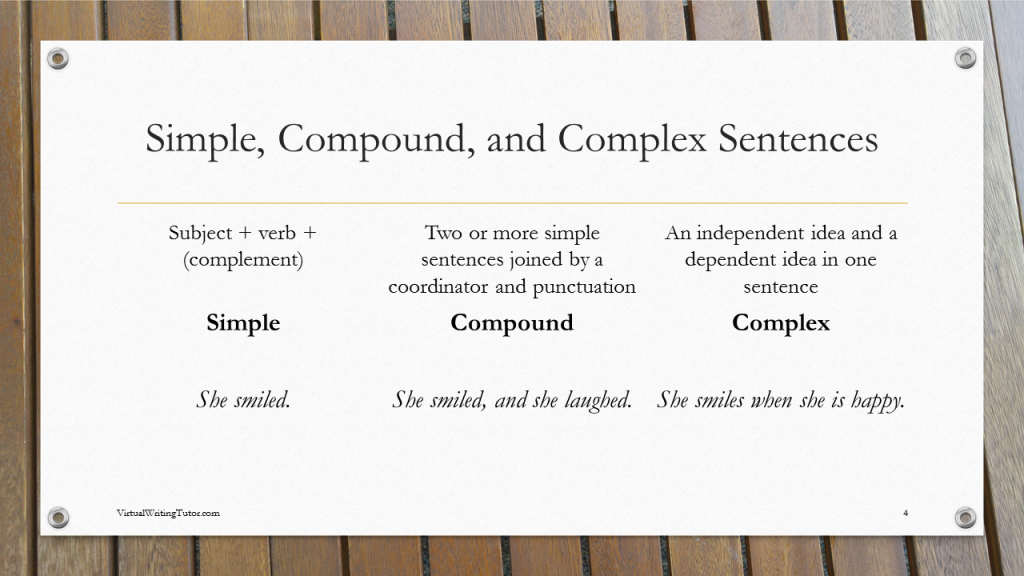
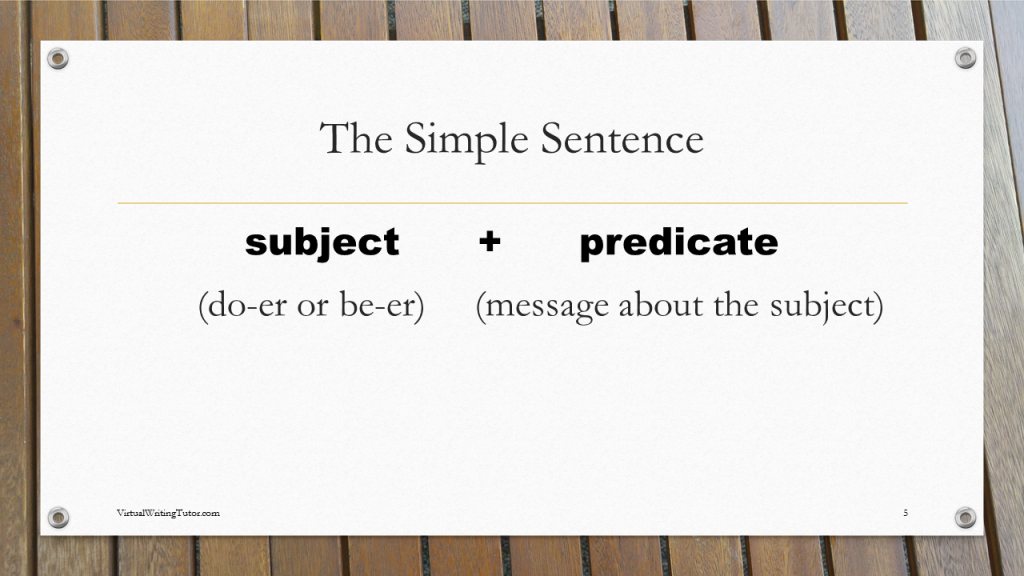
What is a simple sentence?
A simple sentence has a subject and a verb and sometimes an object or complement. The subject is who or what the sentence is about. The verb and the object or complement together are often called the predicate. A simple sentence has two parts: its subject and its predicate.
She smiled. (subject + verb)
She looked pretty. (subject + verb + complement)
Simple sentence
What is a compound sentence?
A compound sentence has two or more simple sentences joined together, usually with a comma and a coordinating conjunction.
She smiled, and she laughed. (Two sentences joined with a comma + coordinator.)
Compound sentence.

What is a complex sentence?
A complex sentence is a simple sentence with subordinate clause joined to it. A subordinate clause depends on another clause to complete an idea, so we call subordinate clauses dependent clauses.
She smiles when she is happy. (Independent clause + dependent clause)
Complex sentence

Error Correction Exercise: Learn how to correct comma errors
